Urban beekeeping has blossomed into a widely embraced tradition across bustling cities around the world. As urban landscapes continue to expand, more and more individuals, businesses, and community organizations are discovering the profound benefits that city beekeeping brings. This comprehensive guide dives into the many advantages associated with maintaining hives in urban settings. From environmental enrichment to economic incentives and community involvement, urban beekeeping holds promise not only for enthusiastic beekeepers but also for entire city ecosystems.
Environmental Benefits of Urban Beekeeping
Increased Pollination in City Gardens
As bees move between flowers in urban gardens and parks, they significantly enhance pollination rates. This results in healthier and more abundant blooms, an uptick in fruit and vegetable yield, and the propagation of plant species suited for city climates. Because many urban gardens are isolated by buildings or roads, bees serve as essential connectors, compensating for the lack of other natural pollinators. The presence of hives on rooftops and balconies brings pollinators closer to plants, helping ensure the vibrancy and productivity of urban flora that might otherwise be neglected.
Strengthening Biodiversity in Urban Spaces
One of the key advantages of urban beekeeping is its contribution to biodiversity within metropolitan areas. Bees are incredibly effective at enabling the reproduction of diverse plant species by transferring pollen between them. In turn, this supports a tapestry of insects, birds, and small animals that rely on varied plant life for survival. Beekeeping encourages the planting of pollinator-friendly flowers, establishing green pockets filled with life. The increased presence of bees, and their foraging habits, can transform concrete jungles into thriving ecosystems teeming with interdependent organisms.
Improvement of Air Quality and Microclimates
Bees indirectly support improvements in urban air quality and microclimates through their pollination activities. Enhanced plant growth resulting from increased pollination leads to more green cover, which in turn helps absorb pollutants, regulate temperatures, and promote higher oxygen levels. As more rooftops and gardens incorporate bee-friendly plantings, these spaces can offer cool retreats from the urban heat, mitigating the effects of the urban heat island while also serving as attractive habitats for various species.
Boosting Community Garden Yields
When beehives are maintained close to community gardens and small urban farms, the plants in those spaces experience a considerable increase in productivity. Bees’ efficient pollination leads to more abundant harvests of fruits, vegetables, and herbs. For city dwellers with limited space and resources, even modest improvements in garden yields are meaningful. Bees help balance urban food systems by making local produce more accessible and reliable, bolstering both nutrition and self-sufficiency.
Producing Hyper-Local Honey and Bee Products
Urban hives offer the unique advantage of hyper-local food production. City beekeepers can harvest honey, beeswax, and sometimes even propolis or pollen from their own neighborhoods. These products have unique flavor profiles which reflect the diverse blooms of the city. The accessibility of freshly harvested, local honey is a boon for residents seeking natural sweeteners and artisanal food products. Urban honey also tends to bypass some agricultural chemicals prevalent in traditional farming regions, offering a cleaner and often more desirable product.
Supporting Urban Agriculture Initiatives
By integrating beekeeping into urban agriculture projects, cities can create more resilient food infrastructure. Beehives complement other forms of city farming, such as vegetable plots, orchards, and rooftop gardens, supporting plant diversity and productivity. Bees act as linchpins that tie together various components of urban agricultural systems, ensuring optimal performance and growth. Their presence demonstrates the symbiotic interdependence between animals and crops, a relationship that is essential for sustainable city food solutions.
Community Engagement and Education
The presence of beehives in urban areas inspires residents to become stewards of their local environment. Through workshops, demonstrations, and hive tours, people learn about pollinator importance, responsible gardening, and ecological balance. Beekeepers become ambassadors for biodiversity, encouraging others to participate in planting pollinator-friendly species and reducing pesticide use. Over time, these collective efforts can reshape attitudes toward urban wilderness and cultivate lasting partnerships among neighbors.
Economic Value and Enterprise Potential
Local Honey and Specialty Product Sales
Urban beekeepers can sell honey, wax, and specialty products to neighbors, farmers markets, or local retailers. City dwellers often value hyper-local honey for its flavor and traceability, creating robust demand for small-batch offerings. Beeswax can be used for candles, soaps, and cosmetics which appeal to eco-conscious consumers. Urban hives often yield premium products, allowing beekeepers to command competitive prices and establish loyal customer bases, thus generating sustainable income streams.
Eco-Tourism and Experience-Based Services
With increasing interest in sustainable living and urban agri-tourism, city apiaries can attract visitors seeking authentic, educational experiences. Offering hive tours, honey tastings, and beekeeping classes enables urban keepers to monetize their expertise. These activities can draw tourists, students, and urban nature enthusiasts, providing a revenue avenue while amplifying environmental awareness. As more people seek immersive and eco-friendly experiences, beekeeping showcases become valued parts of city tourism initiatives.
Incentives and Grants for Sustainable Ventures
Some cities and government bodies provide grants, tax breaks, or incentives to promote urban agriculture and pollinator support. Urban beekeepers may qualify for financial resources that help offset start-up costs, purchase equipment, or fund educational outreach. Nonprofit organizations, foundations, and local councils also award micro-grants for green projects, turning beekeeping into a viable and self-sustaining venture. These incentives can ease entry barriers, making hive management accessible to a broader range of people.
Access to Fresh, Unprocessed Honey
One of the most immediate health benefits for urban beekeepers is the availability of fresh, untreated honey. Raw honey retains natural enzymes, antioxidants, and antimicrobials often lost during commercial processing. City residents who source honey directly from local hives gain the advantage of consuming a wholesome sweetener with potential health-enhancing properties. Anecdotal evidence even points to the use of local honey in reducing allergies, though formal research continues on this topic.
Therapeutic Benefits of Beekeeping
Engaging in beekeeping provides unique therapeutic rewards. Tending hives requires mindfulness, patience, and purposeful movement, which can reduce anxiety and stress. Many urban beekeepers find that working with bees becomes a meditative practice, offering respite from city noise and daily demands. Interacting with bees nurtures a deeper connection to nature, fostering emotional well-being, satisfaction, and a sense of accomplishment as hives flourish.
Promoting Urban Green Spaces for Recreation
Urban beekeeping often goes hand in hand with the creation of new green spaces or enhancement of existing ones. Parks, rooftops, and gardens that host hives become havens for recreation, relaxation, and social gatherings. These biodiverse areas offer urban residents a much-needed escape from concrete surroundings, encouraging exercise, play, and community events. The positive influence of green, bee-friendly environments bolsters both individual and collective well-being.
Previous
Next
Technological Innovations and Adaptability
With limited horizontal space, urban beekeepers have pioneered rooftop and vertical hive systems. These innovative solutions allow hives to flourish above the city streets, making use of otherwise neglected flat rooftops and vertical gardens. By elevating hives, beekeepers protect colonies from ground-level disturbances and maximize exposure to sun and airflow. These systems demonstrate the adaptability of bees and beekeepers alike and open up vast untapped locations for apiaries in even the densest cities.
Overcoming Urban Challenges Responsibly
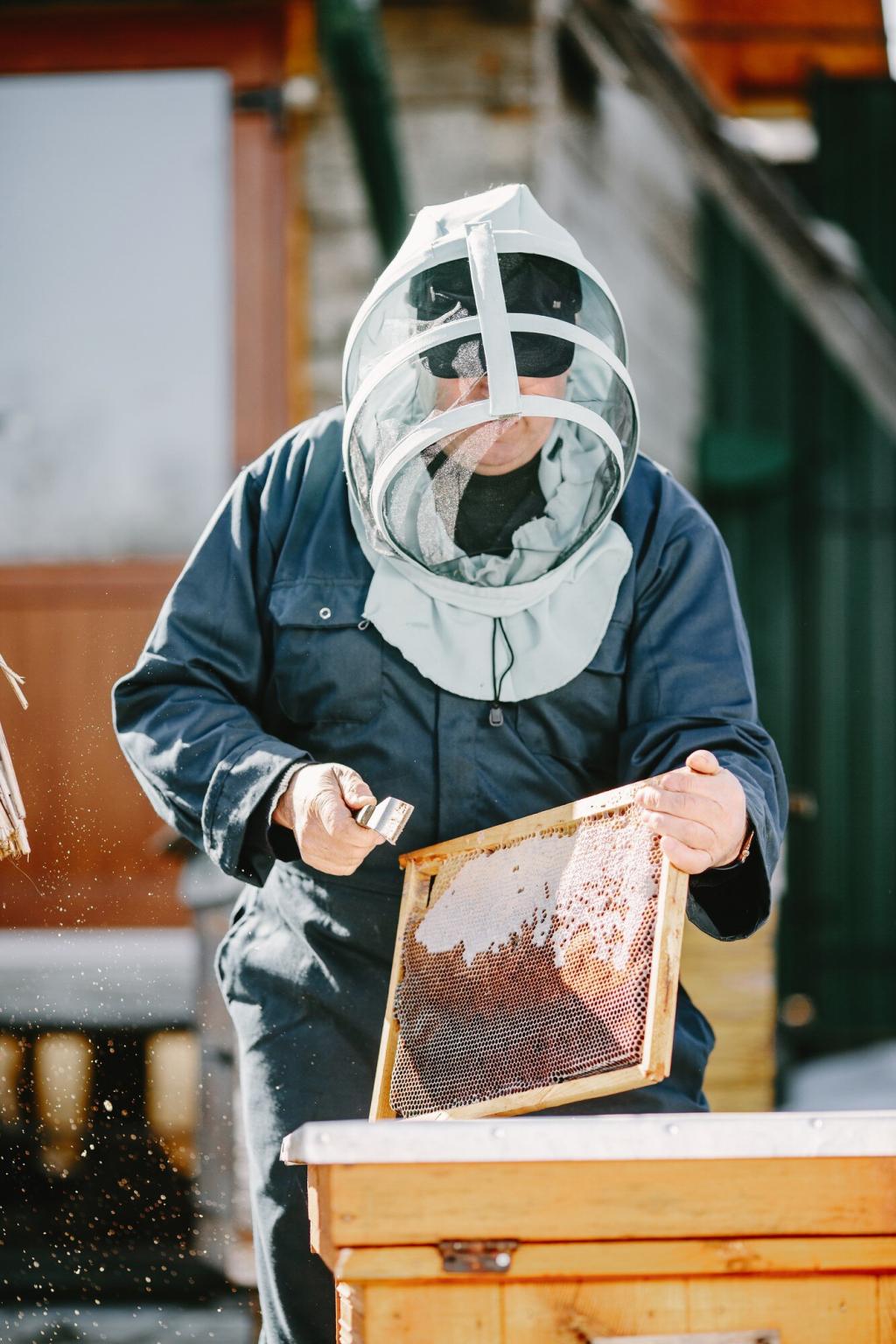

Urban beekeepers must adhere to city ordinances and zoning laws that govern hive placement, registration, and management. Clear communication with neighbors and local officials helps preempt misunderstandings and builds community support. By respecting legal frameworks and proactively addressing concerns about safety or nuisance, beekeepers help foster goodwill and minimize conflict, paving the way for positive public perception of urban hives.